TOP NOVA ORTHODONTICS
Sleep Apnea Treatment: Definition, Causes, and Symptoms
What is Sleep Apnea Treatment? Definition, Causes, and Symptoms:
Sterling, VA
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where the person’s breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep. The word “apnea” means “without breath” in Greek.
Are There Different Types Of Sleep Apnea?
Yes, in fact there are three major types of sleep apnea. Let’s take a closer look at theses three types of sleep apnea and their causes.
1. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea. It occurs when the muscles at the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open during sleep. As a result, the person may experience pauses in breathing, snoring, and gasping for air. This can happen multiple times per hour throughout the night, leading to interrupted sleep and daytime fatigue.
Some of the most common risk factors for OSA include being overweight or obese, having a thick neck circumference, having a narrow airway, being male, being over the age of 40, having a family history of sleep apnea, smoking or using tobacco, and drinking alcohol or taking sedatives.
2. Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a less common type of sleep apnea that occurs when the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing during sleep. This can result in pauses in breathing, snoring, and gasping for air, similar to OSA. However, the underlying cause of CSA is different.
Central sleep apnea is often caused by underlying medical conditions, such as heart failure, stroke, or kidney failure. It can also be caused by the use of certain medications, such as opioids or benzodiazepines.
3. Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome (CSAS)
Complex sleep apnea syndrome (CSAS) is a combination of OSA and CSA. This type of sleep apnea occurs when a person with OSA is treated with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, but their central sleep apnea symptoms persist or worsen. In some cases, treatment with a different type of positive airway pressure therapy may be necessary.
Sleep Apnea: The Hidden Dangers
Sleep apnea is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. People with sleep apnea are at a higher risk of developing:
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Memory problems
Sleep Apnea: What Are The Complications?
Sleep apnea is a serious condition that can have significant impacts on your health and well-being. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Ignoring sleep apnea can lead to chronic fatigue, decreased productivity, and poor quality of life. The interrupted sleep caused by sleep apnea can leave you feeling tired and irritable throughout the day, making it difficult to focus on work or other activities.
- Sleep apnea can also increase your risk of accidents at work or while driving. The excessive daytime sleepiness that often accompanies sleep apnea can impair your ability to concentrate and react quickly, which can be dangerous in certain situations.
- Untreated sleep apnea can also lead to more serious health problems like high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. When the body is deprived of oxygen during sleep, it can trigger a fight-or-flight response. This can cause the body to release stress hormones that can increase blood pressure and heart rate. Over time, this can put a strain on the heart and increase the risk of developing heart disease.
- Sleep apnea can lead to developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.

The Link Between Orthodontics and Sleep Apnea
The reason why orthodontic treatments can be effective for treating sleep apnea is that the alignment of the teeth and jaws can have a direct impact on the airway. When the teeth and jaws are misaligned, it can cause the airway to become narrower, making it more difficult to breathe during sleep. This can increase the risk of sleep apnea and other sleep-related breathing disorders.
Orthodontic treatments such as braces or palatal expanders work by applying gentle pressure to the teeth and jaws, gradually shifting them into the correct alignment. This can help to widen the airway and improve breathing, which can reduce the symptoms of sleep apnea. Additionally, orthodontic treatments can also help to correct any underlying structural issues in the mouth and throat that may be contributing to sleep apnea.
For example, if the lower jaw is set too far back, it can cause the airway to become narrower and increase the risk of sleep apnea. In these cases, orthodontic treatment can be used to bring the lower jaw forward into a more optimal position, which can help to open up the airway and improve breathing.
Orthodontic treatments can also be effective for children and adolescents who may be at risk of developing sleep apnea. In some cases, orthodontic treatment can be used to correct any underlying structural issues before they become more serious, helping to prevent sleep apnea from developing in the future.
Overall, orthodontic treatments can be an effective and non-invasive way to treat sleep apnea, particularly for individuals with mild to moderate sleep apnea. If you are experiencing symptoms of sleep apnea, it’s important to talk to your doctor or a qualified orthodontist to discuss your treatment options.
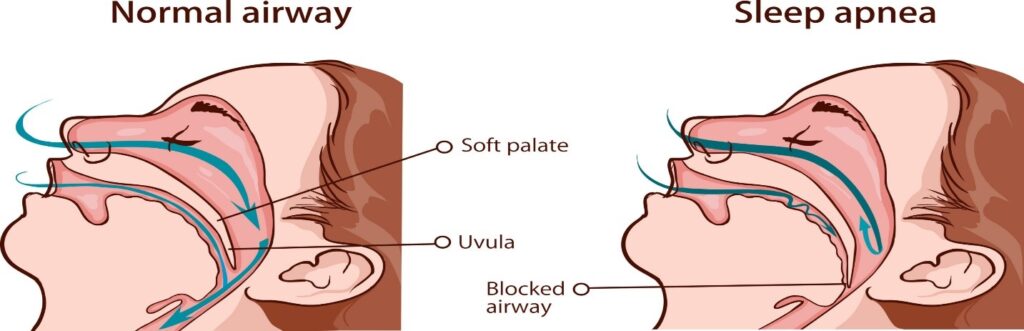
Symptoms: How to Know If You Have Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms often occur during sleep. However, there are some signs and symptoms that can indicate the presence of sleep apnea. Here are some common signs and symptoms of sleep apnea:
- Loud snoring
- Pauses in breathing during sleep
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Restless sleep
- Morning headache
- Daytime sleepiness or fatigue
- Irritability or mood changes
- Difficulty concentrating
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to talk to your doctor. Your doctor may refer you to a sleep specialist who can perform a sleep study to diagnose sleep apnea. A sleep study involves spending a night in a sleep lab, where your breathing and other vital signs will be monitored.
In addition to the signs and symptoms of sleep apnea, there are also certain risk factors that can increase your likelihood of developing this condition. These risk factors include:
- Being overweight or obese: Excess weight can cause fat deposits around the upper airway, which can obstruct breathing and increase the risk of sleep apnea.
- Having a thick neck circumference: A thick neck can indicate excess soft tissue in the throat, which can narrow the airway and increase the risk of sleep apnea.
- Having a narrow airway: A naturally narrow airway or structural abnormalities in the nose, mouth, or throat can increase the risk of sleep apnea.
- Being male: Men are more likely than women to develop sleep apnea, although women can also be affected.
- Being over the age of 40: The risk of sleep apnea increases with age, although children and young adults can also develop this condition.
- Having a family history of sleep apnea: Sleep apnea can run in families, so if you have a family history of this condition, you may be more likely to develop it.
- Smoking or using tobacco: Smoking can cause inflammation and fluid retention in the airway, which can increase the risk of sleep apnea.
- Drinking alcohol or taking sedatives: Alcohol and sedatives can relax the muscles in the throat, which can make it more difficult to breathe and increase the risk of sleep apnea.
It’s important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that you will develop sleep apnea. However, if you have one or more of these risk factors and are experiencing symptoms of sleep apnea, it’s important to talk to your doctor about the possibility of this condition. With early diagnosis and treatment, people with sleep apnea can improve their quality of life and reduce their risk of developing serious health problems.

Treating Sleep Apnea: Options and Effectiveness
There are several treatment options available for sleep apnea. The most common treatment is Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, which involves wearing a mask that delivers pressurized air to keep the airway open during sleep. Other treatment options include:
- Oral appliances
- Surgery
- Lifestyle changes
In addition to these traditional treatment options, orthodontic treatment can also be an effective way to treat sleep apnea. Orthodontic treatment involves the use of devices such as braces or oral appliances to correct the alignment of the teeth and jaws. This can help to improve the airway and reduce the symptoms of sleep apnea.
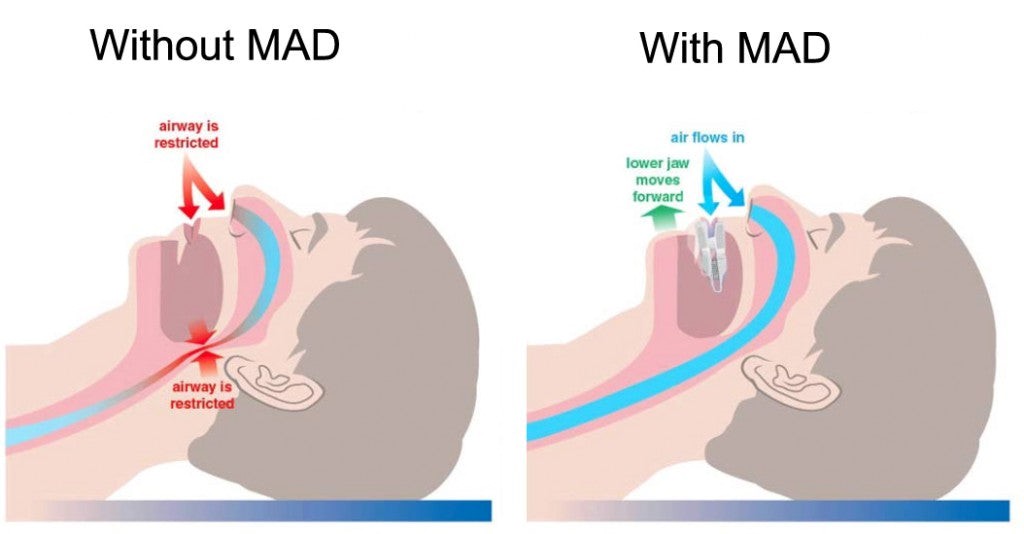
One type of orthodontic appliance that is commonly used to treat sleep apnea is a mandibular advancement device (MAD). This is a custom-fitted oral appliance that is worn over the teeth while sleeping. The MAD works by holding the lower jaw in a forward position, which helps to keep the airway open and prevent the collapse of the soft tissues in the throat.
Studies have shown that MADs can be an effective treatment option for mild to moderate sleep apnea. In fact, some studies have shown that MADs can be just as effective as CPAP therapy in reducing symptoms of sleep apnea, such as snoring and daytime sleepiness.
In addition to MADs, other types of orthodontic treatment may also be beneficial for sleep apnea. For example, orthodontic treatment to correct the alignment of the teeth and jaws can help to improve the airway and reduce the risk of sleep apnea. This may involve the use of braces, aligners, or other orthodontic appliances. The effectiveness of treatment options may vary depending on the severity of sleep apnea and the individual’s health status.
Sleep Apnea in Children: What Parents Need to Know
Sleep apnea can also affect children. Children with sleep apnea may experience behavioral problems, hyperactivity, and difficulty concentrating. If your child is snoring or has trouble sleeping, it’s important to talk to your pediatrician.
Living with Sleep Apnea: Tips for Coping and Improving Quality of Life
Living with sleep apnea can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to improve your quality of life. Here are some tips:
- Use your CPAP machine consistently: If you have been prescribed a CPAP machine, it’s important to use it consistently to get the maximum benefits.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding alcohol and smoking can help improve symptoms of sleep apnea.
- Sleep on your side: Sleeping on your side can help prevent the airway from collapsing and improve breathing.
- Practice good sleep hygiene: Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help improve the quality of your sleep.
- Seek support: Joining a support group or talking to others who have sleep apnea can help you cope with the challenges of living with this condition.

